Hello! We are Danielle and Jessica and we are students from the University of Alberta.
We are both completing our Bachelor of Physical Education degree with our practicum here at Pivotal Physiotherapy, Northgate location. We are interested in educating patients on typical motor vehicle injuries and rehabilitation processes. There are a number of patients experiencing effects from motor vehicle accidents (MVA) and we believe that having information readily available would be helpful. Education is a big part of treatment and rehabilitation, so having access to this information would be beneficial for patients to be actively involved in and understand their recovery.
What’s Next after I’ve been involved in a MVA?
Within 10 days of the collision:
1) File an injury accident report with the police, separate from a vehicle damage report
2) Book an appointment with a primary health care provider (PHCP). Important: ensure that you have filed your injury claim and have received a claim number first
3) File appropriate accident benefit forms available from PHCP or insurer
TIPS:
- Do not delay getting treatment, you may not feel the pain at first
- Set up an assessment/appointment at a rehab clinic as soon as you get your claim number
- Fill out the appropriate accident benefit forms (AB1)
- AB1: Notice of Loss and Proof of Claim
Your Physiotherapist will fill out the following forms (AB2, AB3, AB4)
- AB2: Treatment Plan and Confirmation of Services Provided
- AB3: Progress Report. If more therapy is required this form will be filled out to determine if more treatment will be granted.
- AB4: Concluding Report. After the allotted time, reassessment will take place to determine recovery progress and future treatment plan.
TOP 5 MVA Injuries
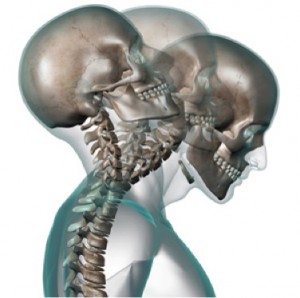
1) Neck Injuries- Whip Lash
Whiplash results when the neck extends beyond its typical range of motion due to a collision. The head is rapidly forced forward or to the side putting pressure on the ligaments of the neck causing sprains and/or strains.
– Sprains= Stretch or tear of a ligament
– Strains= Stretch or tear of a muscle and/or tendon
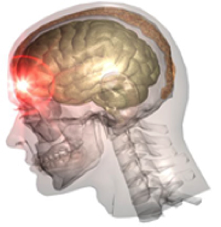
2) Head Injuries- TMD and Concussion
A. TMD= Temporomandibular Disorder. Disk displacement/damage, inflammation or spasm caused by trauma to the TMJ joint
B. Concussion= A traumatic brain injury that alters the way the brain functions, typically due to a forceful impact to the head or violent jarring of the body
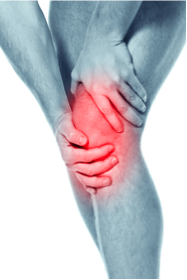
3) Leg and Knee Injuries- Dashboard Injuries
A. Dashboard Injuries= an injury occurring when lower leg contact is made with the dashboard of your vehicle
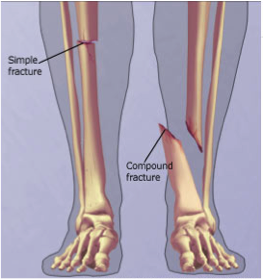
4) Broken Bones and Compound Fractures
A. Compound Fracture= A bony break when the bone itself has punctured the skin
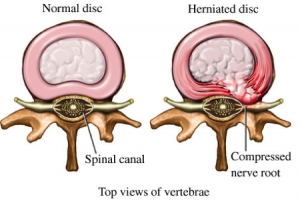
5) Back Injuries- Strains, Disk Herniation, Prolapses
A. Disc Herniation= Soft cushion (disk) between vertebrae bulges out.
B. Disk Prolapse= When the bulging disk irritates the nerve.
Rehab for Bones and Soft Tissue Injuries
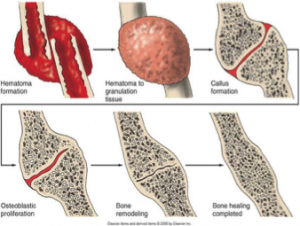
Bones: Symptoms include swelling or bruising over the bone, deformity, pain that worsens with movement or pressure, loss of function, and in compound or open fracture bones protrude from the skin.
After a traumatic incident, go to the hospital or doctor and get the bone reset. They will put you into an immobilization device for 4-6 weeks so that the bones can heal properly.
Once at physiotherapy, the physiotherapist will go through different measurements such as Range of Motion, strength, pain, flexibility, and function. From this information, the physiotherapist can formulate a treatment plan. Modalities such as Interferential Current and Ultrasound may be used to help with pain and swelling. Scar massages over surgical sites can be utilized to remove scar adhesions and improve the mobility.
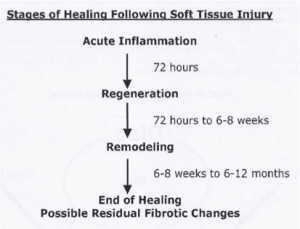
Soft Tissue: Symptoms typically include pain, discomfort, bruising, and restricted range of motion.
- Personal treatment involves RICE (Rest, ice, compress and elevate).
- Once at physiotherapy, you may receive treatment such as massage, acupuncture, intramuscular stimulation and myofascial release.
Jessica Leduc BPE Student
Danielle Gibeau BPE Student
References:
http://www.albertachiro.com/ieadmin/files/Treatment_for_Motor_Vehicle_Accident_Injuries.pdf
http://www.physioworks.com.au/Injuries-Conditions/Regions/ligament-injury
http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/concussion/basics/symptoms/CON-20019272
http://physicaltherapy.about.com/od/orthopedicsandpt/a/fractures.htm
http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/whiplash/basics/symptoms/con-20033090
http://www.healthline.com/health/whiplash#Overview1
http://www.caraccidentinfo.org/car-accident-basics/common-injuries